
Custom Search
All free : 3D articles 10 : antialiasing
In computer graphics, antialiasing is a software technique for diminishing jaggies - stairstep-like lines that should be smooth. Jaggies occur because the output device, the monitor or printer, doesn't have a high enough resolution to represent a smooth line. Antialiasing reduces the prominence of jaggies by surrounding the stairsteps with intermediate shades of gray (for gray-scaling devices) or color (for color devices). Although this reduces the jagged appearance of the lines, it also makes them fuzzier.
Another method for reducing jaggies is called smoothing, in which the printer changes the size and horizontal alignment of dots to make curves smoother.
Antialiasing is sometimes called oversampling. ...... MORE
Another method for reducing jaggies is called smoothing, in which the printer changes the size and horizontal alignment of dots to make curves smoother.
Antialiasing is sometimes called oversampling. ...... MORE
free : 3D articles 9 : 3D computer graphics software
3D computer graphics software refers to programs used to create 3D computer-generated imagery. There are typically many stages in the "pipeline" that studios use to create 3D objects for film and games, and this article only covers some of the software used. Note that most of the 3D packages have a very plugin-oriented architecture, and high-end plugins costing tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars are often used by studios. Larger studios usually create enormous amounts of proprietary software to run alongside these programs...... MORE
free : 3D articles 8 : Motion capture
Motion capture, motion tracking, or mocap are terms used to describe the process of recording movement and translating the movement onto a digital model. It is used in military, entertainment, sports, and medical applications. In filmmaking it refers to recording actions of human actors, and using that information to animate digital character models in 3D animation. When it includes face, fingers and captures subtle expressions, it is often referred to as performance capture..... MORE
free : 3D articles 7 : Computer animation
Computer animation is the art of creating moving images with the use of computers. It is a subfield of computer graphics and animation. Increasingly it is created by means of 3D computer graphics, though 2D computer graphics are still widely used for stylistic, low bandwidth, and faster real-time rendering needs. Sometimes the target of the animation is the computer itself, but sometimes the target is another medium, such as film. It is also referred to as CGI (Computer-generated imagery or computer-generated imaging), especially when used in films.
To create the illusion of movement, an image is displayed on the computer screen then quickly replaced by a new image that is similar to the previous image, but shifted slightly. This technique is identical to how the illusion of movement is achieved with television and motion pictures.
Computer animation is essentially a digital successor to the art of stop motion animation of 3D models and frame-by-frame animation of 2D illustrations. For 3D animations, objects (models) are built on the computer monitor (modeled) and 3D figures are rigged with a virtual skeleton. For 2D figure animations, separate objects (illustrations) and separate transparent layers are used, with or without a virtual skeleton. Then the limbs, eyes, mouth, clothes, etc. of the figure are moved by the animator on key frames. The differences in appearance between key frames are automatically calculated by the computer in a process known as tweening or morphing. Finally, the animation is rendered.
For 3D animations, all frames must be rendered after modeling is complete. For 2D vector animations, the rendering process is the key frame illustration process, while tweened frames are rendered as needed. For pre-recorded presentations, the rendered frames are transferred to a different format or medium such as film or digital video. The frames may also be rendered in real time as they are presented to the end-user audience. Low bandwidth animations transmitted via the internet (e.g. 2D Flash, X3D) often use software on the end-users computer to render in real time as an alternative to streaming or pre-loaded high bandwidth animations.... MORE
To create the illusion of movement, an image is displayed on the computer screen then quickly replaced by a new image that is similar to the previous image, but shifted slightly. This technique is identical to how the illusion of movement is achieved with television and motion pictures.
Computer animation is essentially a digital successor to the art of stop motion animation of 3D models and frame-by-frame animation of 2D illustrations. For 3D animations, objects (models) are built on the computer monitor (modeled) and 3D figures are rigged with a virtual skeleton. For 2D figure animations, separate objects (illustrations) and separate transparent layers are used, with or without a virtual skeleton. Then the limbs, eyes, mouth, clothes, etc. of the figure are moved by the animator on key frames. The differences in appearance between key frames are automatically calculated by the computer in a process known as tweening or morphing. Finally, the animation is rendered.
For 3D animations, all frames must be rendered after modeling is complete. For 2D vector animations, the rendering process is the key frame illustration process, while tweened frames are rendered as needed. For pre-recorded presentations, the rendered frames are transferred to a different format or medium such as film or digital video. The frames may also be rendered in real time as they are presented to the end-user audience. Low bandwidth animations transmitted via the internet (e.g. 2D Flash, X3D) often use software on the end-users computer to render in real time as an alternative to streaming or pre-loaded high bandwidth animations.... MORE
free : 3D articles 7 : Texture mapping
Texture mapping is a method for adding detail, surface texture, or colour to a computer-generated graphic or 3D model. Its application to 3D graphics was pioneered by Dr Edwin Catmull in his Ph.D. thesis of 1974.
A texture map is applied (mapped) to the surface of a shape, or polygon. This process is akin to applying patterned paper to a plain white box.
Multitexturing is the use of more than one texture at a time on a polygon. For instance, a light map texture may be used to light a surface as an alternative to recalculating that lighting every time the surface is rendered. Another multitexture technique is bump mapping, which allows a texture to directly control the facing direction of a surface for the purposes of its lighting calculations; it can give a very good appearance of a complex surface, such as tree bark or rough concrete, that takes on lighting detail in addition to the usual detailed coloring. Bump mapping has become popular in recent video games as graphics hardware has become powerful enough to accommodate it... MORE
A texture map is applied (mapped) to the surface of a shape, or polygon. This process is akin to applying patterned paper to a plain white box.
Multitexturing is the use of more than one texture at a time on a polygon. For instance, a light map texture may be used to light a surface as an alternative to recalculating that lighting every time the surface is rendered. Another multitexture technique is bump mapping, which allows a texture to directly control the facing direction of a surface for the purposes of its lighting calculations; it can give a very good appearance of a complex surface, such as tree bark or rough concrete, that takes on lighting detail in addition to the usual detailed coloring. Bump mapping has become popular in recent video games as graphics hardware has become powerful enough to accommodate it... MORE
free : 3D articles 6 : 3D in Real time
Real-time
Rendering for interactive media, such as games and simulations, is calculated and displayed in real time, at rates of approximately 20 to 120 frames per second. In real-time rendering, the goal is to show as much information as possible as the eye can process in a 30th of a second (or one frame, in the case of 30 frame-per-second animation). The goal here is primarily speed and not photo-realism. In fact, here exploitations are made in the way the eye 'perceives' the world, and as a result the final image presented is not necessarily that of the real-world, but one close enough for the human eye to tolerate. Rendering software may simulate such visual effects as lens flares, depth of field or motion blur. These are attempts to simulate visual phenomena resulting from the optical characteristics of cameras and of the human eye. These effects can lend an element of realism to a scene, even if the effect is merely a simulated artifact of a camera. This is the basic method employed in games, interactive worlds, VRML. The rapid increase in computer processing power has allowed a progressively higher degree of realism even for real-time rendering, including techniques such as HDR rendering. Real-time rendering is often polygonal and aided by the computer's GPU... MORE
Rendering for interactive media, such as games and simulations, is calculated and displayed in real time, at rates of approximately 20 to 120 frames per second. In real-time rendering, the goal is to show as much information as possible as the eye can process in a 30th of a second (or one frame, in the case of 30 frame-per-second animation). The goal here is primarily speed and not photo-realism. In fact, here exploitations are made in the way the eye 'perceives' the world, and as a result the final image presented is not necessarily that of the real-world, but one close enough for the human eye to tolerate. Rendering software may simulate such visual effects as lens flares, depth of field or motion blur. These are attempts to simulate visual phenomena resulting from the optical characteristics of cameras and of the human eye. These effects can lend an element of realism to a scene, even if the effect is merely a simulated artifact of a camera. This is the basic method employed in games, interactive worlds, VRML. The rapid increase in computer processing power has allowed a progressively higher degree of realism even for real-time rendering, including techniques such as HDR rendering. Real-time rendering is often polygonal and aided by the computer's GPU... MORE
free : 3D articles 5 : 3D rendering
Rendering is the final process of creating the actual 2D image or animation from the prepared scene. This can be compared to taking a photo or filming the scene after the setup is finished in real life. Several different, and often specialized, rendering methods have been developed. These range from the distinctly non-realistic wireframe rendering through polygon-based rendering, to more advanced techniques such as: scanline rendering, ray tracing, or radiosity. Rendering may take from seconds to days for a single image/frame. In general, different methods are better suited for either photo-realistic rendering, or real-time rendering.. MORE
free : 3D articles 4 : 3D modeling
In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical, wireframe representation of any three-dimensional object (either inanimate or living) via specialized software. The product is called a 3D model. It can be displayed as a two-dimensional image through a process called 3D rendering or used in a computer simulation of physical phenomena. The model can also be physically created using 3D Printing devices.
Models may be created automatically or manually. The manual modeling process of preparing geometric data for 3D computer graphics is similar to plastic arts such as sculpting. MORE
free : 3D articles 3 : 3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics (in contrast to 2D computer graphics) are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering 2D images. Such images may be for later display or for real-time viewing. Despite these differences, 3D computer graphics rely on many of the same algorithms as 2D computer vector graphics in the wire-frame model and 2D computer raster graphics in the final rendered display. In computer graphics software, the distinction between 2D and 3D is occasionally blurred; 2D applications may use 3D techniques to achieve effects such as lighting, and primarily 3D may use 2D rendering techniques. 3D computer graphics are often referred to as 3D models. Apart from the rendered graphic, the model is contained within the graphical data file. However, there are differences. A 3D model is the mathematical representation of any three-dimensional object (either inanimate or living). A model is not technically a graphic until it is visually displayed. Due to 3D printing, 3D models are not confined to virtual space. A model can be displayed visually as a two-dimensional image through a process called 3D rendering, or used in non-graphical computer simulations and calculations. MORE
free : Best 3d images 6 (digital art) : Ghost ship series, Full moon rising
title: Ghost ship series: Full moon rising (from http://fantasyartdesign.com)
description: You might not be aware that ghost ships have existed for centuries. Some ghost ships supposed to be crewed by the dead, while some ghost ships are real ships that have disappeared or sunk tragically. Full Moons associated with temporal insanity.
description: You might not be aware that ghost ships have existed for centuries. Some ghost ships supposed to be crewed by the dead, while some ghost ships are real ships that have disappeared or sunk tragically. Full Moons associated with temporal insanity.
free : Best 3d photos 5 (digital art) : The island of lost hopes
title: The island of lost hopes (from http://fantasyartdesign.com)
description: I used the famous Antoni Gaudi architecture of the massive Roman Catholic Church of the Sagrada Familia which construction began in 1882
description: I used the famous Antoni Gaudi architecture of the massive Roman Catholic Church of the Sagrada Familia which construction began in 1882
free : Best 3d pictures 4 (digital art) : Final Frontier Voyager (FES) The Flat Earth Society
title: Final Frontier Voyager (FES) The Flat Earth Society (from http://fantasyartdesign.com)
description: History of the flat-earth Theory. The long association between Christianity and the flat-earth theory begins in the sixth century when a Greek monk of Alexandria, Cosmas, who had traveled widely in the East, retired to a cloister in Sinai.
description: History of the flat-earth Theory. The long association between Christianity and the flat-earth theory begins in the sixth century when a Greek monk of Alexandria, Cosmas, who had traveled widely in the East, retired to a cloister in Sinai.
free : Best 3d pictures 3 (digital art) : Bryxeland
title: Bryxeland (from http://fantasyartdesign.com)
description: Fantasy landscape dream surreal, wasteland wilderness fairytale waste imaginative daydream vision scenery Trees artistic scenery countryside land scene backdrop visualization. Digital art 3d fantasy artwork free computer wallpaper picture contemporary.
description: Fantasy landscape dream surreal, wasteland wilderness fairytale waste imaginative daydream vision scenery Trees artistic scenery countryside land scene backdrop visualization. Digital art 3d fantasy artwork free computer wallpaper picture contemporary.
free : Best 3d pictures 2 (digital art) : Fairyland

title: Fairyland (from http://fantasyartdesign.com)
description: Landscape castle waterfall scenery countryside cascade land scene backdrop Fantasy dream daydream vision visualization fairytale. Computer image 3d digital art wallpaper free fantasy art, fine art picture gallery exhibition. Creative original imaginative
free : Best 3d pictures 1 (digital art) : Mojoland
 title: Mojoland (from http://fantasyartdesign.com)
title: Mojoland (from http://fantasyartdesign.com)
description: Landscape scenery countryside land scene backdrop. Computer desktop digital fantasy art wallpaper gallery modern computer artwork. Creative original imaginative artistic ingenious inspiration. Science fiction sci-fi fiction imaginary futuristic inventive.
free CINEMA 4D videos tutorials 6 : Screw Modeling Part 2
Cinema 4D VIDEO Tutorial - Screw Modeling Part 2 (From: kenykkutube)
It demonstrates how to model a screw using Cinema 4D
previous -- next
free CINEMA 4D videos tutorials 5 : Screw Modeling Part 1
Cinema 4D VIDEO Tutorial - Screw Modeling Part 1 (From: kenykkutube)
It demonstrates how to model a screw using Cinema 4D
free CINEMA 4D videos tutorials 4 : Adding Materials in Cinema 4D
3D Animation in Cinema 4D : Adding Materials in Cinema 4D (From: expertvillage)
How to add materials in Cinema 4D; learn more about animation and rendering software in this free instructional video.
free CINEMA 4D videos tutorials 3 : C4D tutorial FFD
free Bryce videos tutorials 5 : Robby the Robot
FREE Robby the Robot from Forbidden Planet in Bryce!- video tutorial (From: clydesight)
previous -- next
free 3D videos tutorials
 3D Studio Max videos tutorials
3D Studio Max videos tutorialsAnimation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 Maya videos tutorials
Maya videos tutorials
Animation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 Bryce videos tutorials
Bryce videos tutorials
Animation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 Rhino videos tutorials
Rhino videos tutorials
Animation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 CINEMA 4D videos tutorials
CINEMA 4D videos tutorials
Animation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 Blender videos tutorials
Blender videos tutorials
Animation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 LightWave videos tutorials
LightWave videos tutorials
Animation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 Maya videos tutorials
Maya videos tutorialsAnimation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 Bryce videos tutorials
Bryce videos tutorialsAnimation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 Rhino videos tutorials
Rhino videos tutorialsAnimation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 CINEMA 4D videos tutorials
CINEMA 4D videos tutorialsAnimation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 Blender videos tutorials
Blender videos tutorialsAnimation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
 LightWave videos tutorials
LightWave videos tutorialsAnimation, Modeling, Lighting, Materials/Textures, Effects, Rendering...
free 3D tools : 3D Screen Creator (3)
3D Screen Creator from devsoft.ch

3D Screen Creator is a tool to create 3D real time animations or screensavers.
You can create your own executable or your own screensaver using only a visualinterface and without any line of code.
You can import your 3D objects from your favorite 3D package (3DStudio, Lightwave, ...) and use
it directly into 3D Screen Creator. You can also create 2D Slideshow using the power of your
3D card to create stunning transition effects.
Create your own world using your objects or one of the multiple primitive (cube, torus, cylinder...) included
in 3D Screen Creator, add a terrain using an heightmap, set the position of your camera and simply create
a full installable screen saver in a few clicks.
free Virtual Reality Toolbox™ 4.7 (6)
Virtual Reality Toolbox™ 4.7 from mathworks.com
Animate and visualize Simulink systems in three dimensions
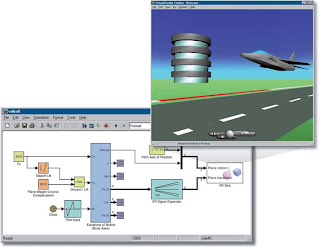
Model of an airplane during takeoff, created using Simulink. The Virtual Reality Toolbox animates the virtual world in the Web browser window during simulation.
The Virtual Reality Toolbox™ lets you view and interact with dynamic system simulations in a 3-D virtual reality environment. The toolbox links MATLAB® and Simulink® with virtual reality graphics, enabling MATLAB or Simulink to control the position, rotation, and dimensions of the 3-D images defined in the virtual reality environment. The result is a presentation-quality 3-D animation.
Through visualization, the Virtual Reality Toolbox product provides insight into the dynamic systems that you model in Simulink. You can use these viewing capabilities in automotive, aerospace, communication, biological, and mechanical applications. Read more
Animate and visualize Simulink systems in three dimensions

Model of an airplane during takeoff, created using Simulink. The Virtual Reality Toolbox animates the virtual world in the Web browser window during simulation.
The Virtual Reality Toolbox™ lets you view and interact with dynamic system simulations in a 3-D virtual reality environment. The toolbox links MATLAB® and Simulink® with virtual reality graphics, enabling MATLAB or Simulink to control the position, rotation, and dimensions of the 3-D images defined in the virtual reality environment. The result is a presentation-quality 3-D animation.
Through visualization, the Virtual Reality Toolbox product provides insight into the dynamic systems that you model in Simulink. You can use these viewing capabilities in automotive, aerospace, communication, biological, and mechanical applications. Read more
free : 3D articles: 3-D Holography Breakthrough: Erase And Rewrite In Minutes (3)
3-D Holography Breakthrough from sciencedaily.com

University of Arizona optical scientists have broken a technological barrier by making three-dimensional holographic displays that can be erased and rewritten in a matter of minutes.
The holographic displays -- which are viewed without special eyewear -- are the first updatable three-dimensional displays with memory ever to be developed, making them ideal tools for medical, industrial and military applications that require "situational awareness."
"This is a new type of device, nothing like the tiny hologram of a dove on your credit card," UA optical sciences professor Nasser Peyghambarian said. "The hologram on your credit card is printed permanently. You cannot erase the image and replace it with an entirely new three-dimensional picture." Read more
"This is a new type of device, nothing like the tiny hologram of a dove on your credit card," UA optical sciences professor Nasser Peyghambarian said. "The hologram on your credit card is printed permanently. You cannot erase the image and replace it with an entirely new three-dimensional picture." Read more
free : 3D articles: 3D Web Search (2)
Introducing 3D Web Search from spacetime.com

Visit your favorite search engine, type in your search term and you may find yourself spending all afternoon clicking
back and forth between a list and the web pages you are looking for. Not anymore. With SpaceTime's™ 3D Web Search, you choose your search engine from the drop down menu, type in your search term and enjoy the experience as SpaceTime™ displays all your search results at once in our patent pending interface. Enjoy the perks that immediate visualization has to offer as you save time, eliminate clicks and find the web pages you are looking for at a fraction of the time. Read More
free : The virtual reality: Project Wonderland: Toolkit for Building 3D Virtual Worlds (4)
Project Wonderland from lg3d-wonderland.dev.java.net
Project Wonderland is a 3D scene manager for creating collaborative virtual worlds. Within those worlds, users can communicate with high-fidelity, immersive audio and can share live applications such as web browsers, OpenOffice documents, and games.

Contributed by: The Project Wonderland Team @ Sun.
The virtual reality : IBM Sensors Link Real World and Virtual World (4)
IBM Sensors Link Real World and Virtual World from 3pointd.com

UgoTrade has a lengthy write-up of some of the work IBM has been doing in the virtual world of Second Life lately. [Via IBM’s Rob Smart.] The blog entry is all about creating links between the real world and the virtual world, so that sensor data and other information can be visualized in Second Life on a real-time basis. In the screenshot above, “The blue balls with white designs represent active Bluetooth devices. The pyramids scattered about the floor represent other people working, with the color designating things like physical presence or telepresence,” according to UgoTrade. This is just one kind of application that could start to make Second Life a much more useful place. I’d love to see entities and conditions being tracked around SL in real time. Why? Because there’s a ton of information to be extracted from a digital environment, which can then be applied to real-world problems from logistics to marketing to sociology, you name it. That said, this won’t start to get really interesting until we have a nearly plug-n-play solution. Which is probably one of the things IBM is working on. Keep your sensors tuned. Read more.
3D tools : Inventor 2D to 3D Tool (2)
Inventor 2D to 3D Tool from labs.blogs.com

The 2D to 3D tool for Autodesk Inventor helps you create 3D models of parts that were designed in 2D. Yesterday we posted an updated version of the tool on Autodesk Labs. The new version is compatible with the Autodesk Inventor LT Technology Preview. Getting to the third dimension is no longer limited to our Autodesk Inventor 2008 or R11 users.
Updating utilities so that a wider variety of mechanical designers can benefit is alive in the lab. Read more
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)




